Dynamic Retinoscopy Methods
Dynamic retinoscopy is also called Near Retinoscopy because it is done while the patient is focusing on a near target(In accommodated state). The main purpose of Dynamic Retinoscopy is to find out the accommodative response of the patient(lag or lead or normal). There are different methods of performing Dynamic Retinoscopy.
- Nott method
- Monocular estimate method
- Near red green
- Dynamic cross cylinder
- Bell’s method
Out of which the two important methods are
Nott Method:
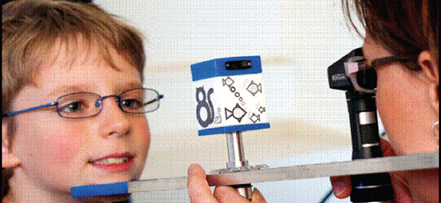
- Target: Near target at subjects working distance. (Near target is either held in patients hand or A scale containing a self-illuminated cube with pictures held as shown in figure 1)
- The patient sees the target binocularly
- Patients must wear their distance correction
- Retinoscope is kept alongside the target and the movement of the reflex is observed
- If the movement is against, then the subject is over accommodating. Move the retinoscope towards the kid till you get neutral point while keeping target fixed. The distance between the neutral point and the target will be converted into dioptres.The resultant dioptric value is the magnitude of the lead of the accommodation.
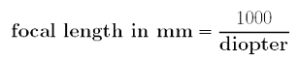
- If the movement is with, then the subject is under accommodating. Move the retinoscope away from the kid till you get neutral point while keeping target fixed. the distance between the neutral point and the target will be converted into dioptres. The resultant dioptric value is the magnitude of the lag of the accommodation.

Monocular Estimate Method(MEM):
- It is also same as Nott method but instead of moving retinoscope front and back, we place lenses to neutralize the reflex.
- Target: Near target attached to the retinoscope at patient working distance.The patient sees it binocularly
- Patients must wear their distance correction.

- If the movement is with add “+ lenses” and for against movement add “- lenses” till the reflex neutralizes.
- If you get final power in ‘– lenses’ then the subject is over accommodating which means the patient has a lead of accommodation.
- If you get final power in’+ lenses’ then the subject is under accommodating which means the patient has a lag of accommodation.
- The normal range of accommodative response is +0.50DS to +0.75 DS.